|
High Speed Networking
What are my choices for
high-speed networking?
Switched Ethernet
Switched Ethernet relies on centralized multiport switches to
provide a physical link between multiple LAN segments. Inside each
intelligent switch, high-speed circuitry supports wire-speed virtual
connections between all the segments for maximum bandwidth
allocation on demand. Adding new segments to a switch increases the
aggregate network speed while reducing overall congestion, so
Switched Ethernet provides superior configuration flexibility. It
also gives you an excellent migration path from 10- to 100-Mbps
Ethernet because both segments can often operate via the same
switch.
Benefits of Switched Ethernet
It's a cost-effective technique for
increasing the overall network throughput and reducing congestion on a
10-Mbps network. Other than the addition of the switching hub, the
Ethernet network remains the same—the same network interface cards, the
same client software, the same LAN cabling.
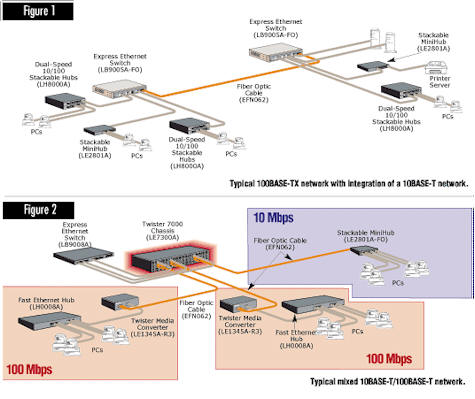
100BASE-T (IEEE 802.3u)
100BASE-T retains the familiar CSMA/CD media access technique used in
10-Mbps Ethernet networks. It also supports a broad range of cabling
options: two standards for twisted pair, one for fiber. 100BASE-TX
supports 2-pair Category 5 UTP or Type 1 STP cable. 100BASE-T4 uses 4-pair
Category 3 or 4 cable. And 100BASE-FX supports fiber optic links via
duplex multimode fiber cable.
Benefits of 100BASE-T
It retains CSMA/CD, so existing network
management systems don't need to be rewritten. It can easily be integrated
into existing 10-Mbps Ethernet LANs, so your previous investment is saved.
It's also backed by hundreds of manufacturers in the high-speed networking
industry.
100VG (IEEE 802.12)
100VG uses an encoding scheme called Quartet Signaling to transmit data
simultaneously over all four pairs in the network cable, so it achieves a
full tenfold increase in transmission speeds over 10BASE-T. It also
replaces the CSMA/CD media access control protocol with Demand Priority to
optimize network operation and eliminate the overhead of packet collisions
and recovery. Demand Priority works like this: The hub directs all
transmissions, acknowledging higher-priority packet requests before
normal-priority requests. This effectively guarantees bandwidth to
time-sensitive applications like voice, video, and multimedia
applications.
Benefits of 100VG
It uses a transmission frequency very similar to traditional Ethernet,
works on any conventional cabling system (Category 3, 4, or 5 UTP, Type 1
STP, and fiber optics), and uses the same connectors. In addition, 100VG
may soon support Token Ring networks—a potential advantage over its rival
standard 100BASE-T.
|
100-Mbps Ethernet Standards |
|
|
| |
 |
100BASE-T (IEEE
802.3u) |
 |
100VG (UEEE 802.12) |
|
Variations of this Standard |
|
100BASE-TX
100BASE-T4
100BASE-FX
|
|
IEEE
802.3 Ethernet Framing
IEEE 802.5 Token Ring
Framing (Pending) |
| Supported
Cable Type |
|
100BASE-TX |
 |
Category 5 (2-Pair) |
|
|
| 100BASE-T4 |
|
Category 3 or 4
(4-Pair) |
Category 3, 4, or 5
(4-Pair) |
| 100BASE-FX |
|
Duplex Multimode or
Single-Mode Fiber |
Duplex Multimode Fiber |
Maximum Cable Segments
(Hub-to-Node) |
|
100BASE-T4 |
|
Category 3 or
4—100 m |
|
Category 3, 4, or 5
(4-Pair)—100 m
Multimode Fiber—2 km |
| 100BASE-TX |
|
Category 5—100 m |
|
| 100BASE-FX |
|
Multimode Fiber—2
km
Single-Mode—10 km |
|
| Best Applications |
|
Backbone using Ethernet
switches to provide increased throughput. Small to medium workgroups
using applications (i.e. CAD, CAM) that output huge data files. |
|
Networks using
extremely time-sensitive data such as videoconferencing or multimedia. |
ATM
Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) is a cell-based fast-packet communication
technique that supports data-transfer rates ranging from sub-T1 speeds
(less than 1.544 Mbps) up to 10 Gbps. Like other packet-switching services
(Frame Relay, SMDS), ATM achieves its high speeds in part by transmitting
data in fixed-size cells and dispensing with error-correction protocols.
Instead, it relies on the inherent integrity of digital lines to ensure
data integrity.
Benefits of ATM
Networks are extremely versatile. An ATM network can be treated as a
single network, whether it connects points in a building or across the
country. Its fixed-length cell-relay operation, the signaling technology
of the future, offers more predictable performance than variable-length
frames. And it can be integrated into an existing network as needed
without having to upgrade the entire LAN.
|
